IntroducingJavaScript Algorithms: What Is Binary Search
Github:
- Repository: algorithms-review
- File: binary-search.js
Notes:
- Binary Search ONLY works with Sorted Arrays.
What Is Binary Search?
A. Binary Search Definition:
In Computer Science, Binary Search (Half-Interval Search) is a Search Algorithm to find a specific element located in an Array (ONLY works with Sorted Arrays). Binary Search is advantageous over a standard Linear Search because it searches faster and more efficiently due to what some developers call as "Dividing and Conquering*" Instead of searching an array at index 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on like we do in a For Loop, Binary Search allows us to divide our search in half each time we look for a target value.
We define a middleIndex or midpoint from the element in the middle of the array (Divide) to see if our target value is greater than or less than the middleIndex or midpoint. Depending on if the target value is greater than or less than the middleIndex, we can remove the left or right of our array from our search (Conquer).
B. Binary Search Gif:
In the example gif below, we want to find the target number "37" in this Sorted Array.
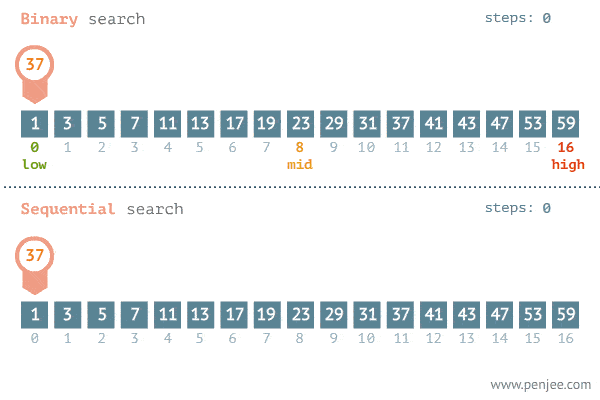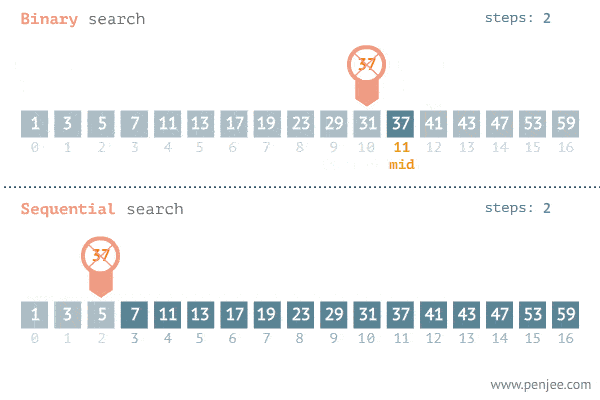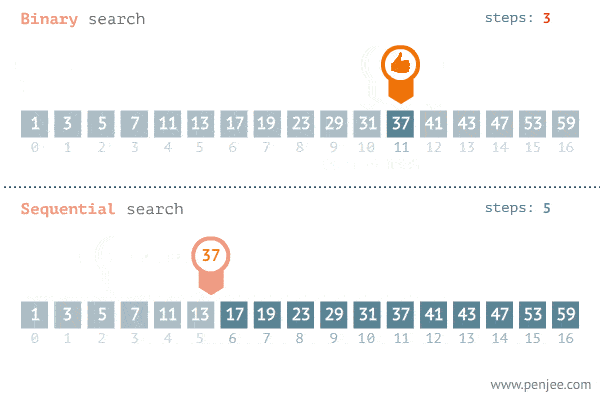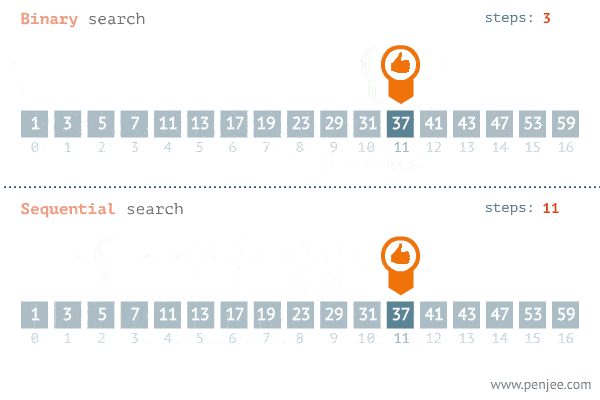
C. Binary Search Step-By-Step Process Breakdown:
In this step-by-step process, we're going to be breaking down how to do a Binary Search on the following "exampleArray." This is the same array from the gif in Step B.
let exampleArray = \[1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59\];
- We are going to need to keep track of the 3 following things as variables to perform a Binary Search: startIndex, middleIndex, and endIndex.
- startIndex will always be 0:
let startIndex = 0; - endIndex can always be calculated using array.length:
let endIndex = array.length - 1; - We want to get an inital middleIndex using the startIndex and endIndex, and the divide by 2. It can be a little tricky due to even or odd number of amount of elements in the array. We can use
Math.floor()to round down orMath.ceil()to round up, but we are going to round down withMath.floor()in our case:let middleIndex = Math.floor((startIndex + endIndex) / 2). This will be the only index variable that we store inside our While Loop. - Our while loop will then repeat the process until it ends. In our case, I have my example using
while(startIndex >= endIndex). - There are 16 total elements in the array, so let's reacp. We divide by 2, round down with Math.floor(), in which picks a middleIndex at Index #8 where the number "37" is located. Using this number "23" we now compare our target number "37" to identify which on is greater than or less than each other.
- If the middeIndex value is less than the target value of 37, we know that our target value will be somewhere to the right of the middleIndex. We can then assign our startIndex variable as the current middleIndex value, essentially chopping off the left half of the array. We also want to increment middleIndex by the count of 1 if our target number “37” > middleIndex “23.”
- If the middeIndex value is greater than the target value of 37, we know that our target value will be somewhere to the left of the middleIndex. We can then assign our endIndex variable as the current middleIndex value, essentially chopping off the right half of the array.** We also want to Decrement middleIndex by the count of 1 if our target number “37” < middleIndex “23.”**
- If the middleIndex value is equal to the target value of 37, we have found our target number “37.” The loop may only loop once or it may loop dozens of times, depending on your array size and what your target number is.
- Congratulations, you’ve completed your Binary Search!
D. Binary Search Code:
The code provided below shows 2 versions:
1. With Comments:
const binarySearch = (array, target) => {
// Define Start and End Index
let startIndex = 0;
let endIndex = array.length - 1;
// While Start Index is less than or equal to End Index
while(startIndex <= endIndex) {
// Define Middle Index (This will change when comparing )
let middleIndex = Math.floor((startIndex + endIndex) / 2);
// Compare Middle Index with Target for match
if(target === array[middleIndex]) {
return console.log("Target was found at index " + middleIndex);
}
// Search Right Side Of Array
if(target > array[middleIndex]) {
console.log("Searching the right side of Array")
// Assign Start Index and increase the Index by 1 to narrow search
startIndex = middleIndex + 1;
}
// Search Left Side Of Array
if(target < array[middleIndex]) {
// Assign End Index and increase the Index by 1 to narrow search
console.log("Searching the left side of array")
endIndex = middleIndex - 1;
}
// Not found in this iteration of the loop. Looping again.
else {
console.log("Not Found this loop iteration. Looping another iteration.")
}
}
// If Target Is Not Found
console.log("Target value not found in array");
}
2. Without Comments:
const binarySearch = (array, target) => {
let startIndex = 0;
let endIndex = array.length - 1;
while(startIndex <= endIndex) {
let middleIndex = Math.floor((startIndex + endIndex) / 2);
if(target === array[middleIndex) {
return console.log("Target was found at index " + middleIndex);
}
if(target > array[middleIndex]) {
console.log("Searching the right side of Array")
startIndex = middleIndex + 1;
}
if(target < array[middleIndex]) {
console.log("Searching the left side of array")
endIndex = middleIndex - 1;
}
else {
console.log("Not Found this loop iteration. Looping another iteration.")
}
}
console.log("Target value not found in array");
}